In world of security, storing password in the back-end database in plaintext is a security design failure as plain text is easily readable by the humans, to overcome this loophole internal application developers use hashing techniques to protect the password from hackers incase of breach of database. These hashes are stored in the local SAM database or Active Directory.
So, what is Hashing Process?
Hashing is the process that converting an input of any length characters into a fixed-size string of text (Hash Value). Hashing is one-way road to enhance the security in other words “It is one-way function, the data that is hashed cannot be unhashed/reversed practically”.
The process of hashing varied from system to system, so let’s dive into Windows Operating System.
Windows use below hashing Function: LANMAN, NTLM
Linux/Unix: SHA256, SHA-512, DES, 3DES, MD5, Blowfish
In this article lets learn more about Hashing process of windows OS.
LANMAN Hashing Process:
LAN Manager (LANMAN) password hash is very weak and legacy password hashing mechanism, it was used in early windows NT system. It was used till windows XP/windows server 2003.It is very prone to bruteforce attack, lets study why it is known as weak mechanism.
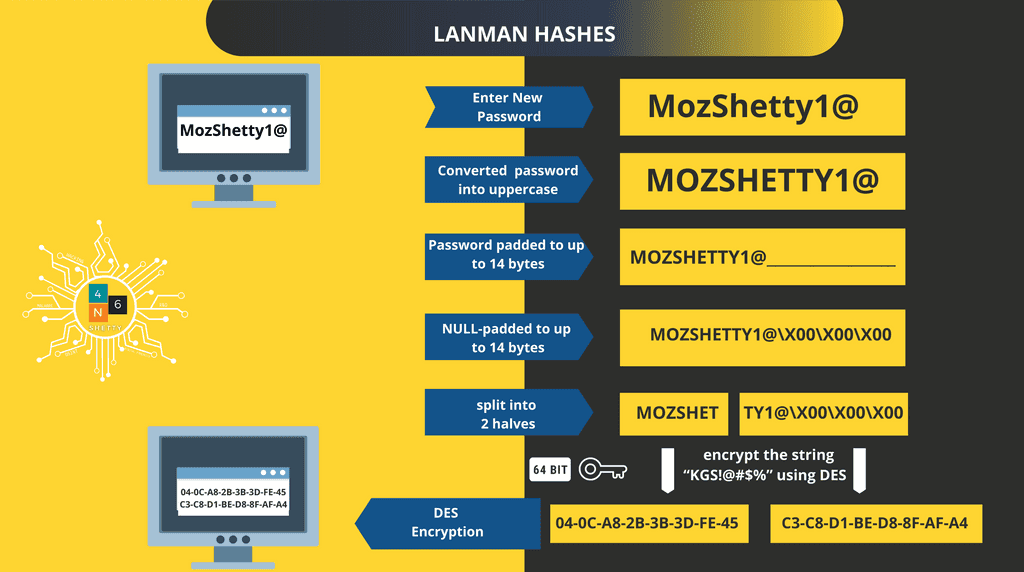
Let’s assume that your password is “MozShetty1@”
Step 1: All the characters are converted into Uppercase.
MoZShetty1@ - > MOZSHETTY
Step 2: Password is padded to 14bytes and added null characters so that its length becomes 14, so the result will be
MOZSHETTY1@\X00\X00\X00
\Xoo represents Null Character.
Step 3: Password is spilt into two 7 Byte Chunks
MOZSHET TY1@\X00\X00\X00
Step 4: – Above 7 Byte keys used as 64-BIT DES Keys (with the addition of a parity bit for every seven bits) and then used to encrypt the string “KGS!@#$%” using DES algorithm in ECB mode.
Step 5: The output of the two DES Encrypted hashes is then concatenated, and that makes out LM hash.
04-0C-A8-2B-3B-3D-FE-45-C3-C8-D1-BE-D8-8F-AF-A4
Disadvantage:
- Case is not preserved
- Prone to Brute Force Attack
- Password is stored in two chuck of 7 byte it is easy for the attacker to recover plain text.
NT Hashes: Modern windows system use NT password hashes, although it is considered as strongest password it doesn’t use salt on other hand we can say its better then LANMAN hashes but not so great in terms of security perspective.
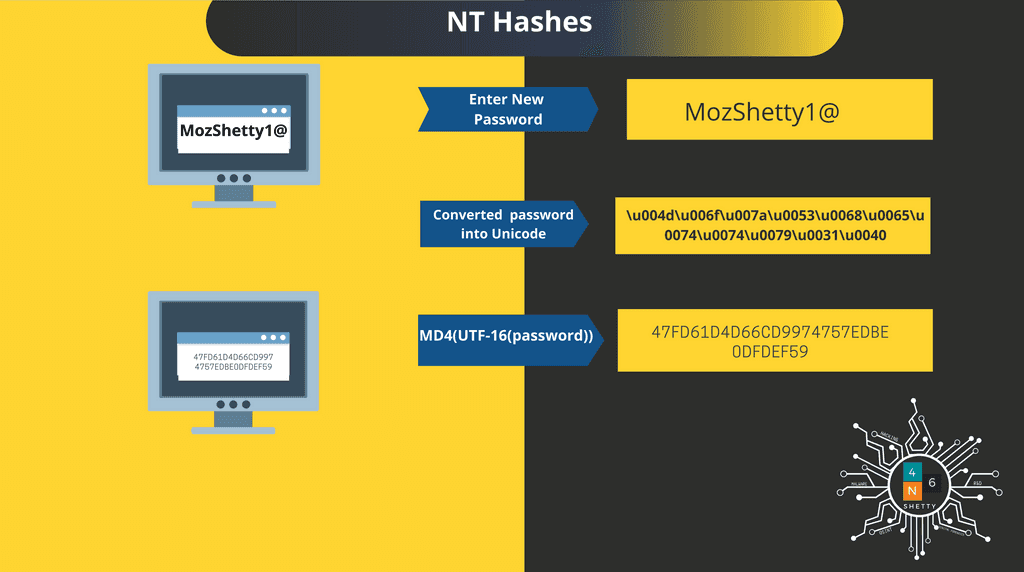
So lets learn how NT hashes mechanism works;
Step1: Password is converted into Unicode
UTF-16(Password)
MozShetty1@ -> \u004d\u006f\u007a\u0053\u0068\u0065\u0074\u0074\u0079\u0031\u0040
Step2: MD4 Hashing Algorithm Used:
MD4(UTF-16(Password))
Step 3: Encrypted using RC4 or AES-CBC-128 in SAM.
Advantages of NT over LANMAN is Case sensitivity is preserved by then no salts is used in NT Hashes, it is prone to pre-computed hashed dictionary attacks.
The simplest way is to use a password that's at least 15 characters long so that No LANMAN has stored only NT hash is used for local authentication.
OS Process to store and calculate the hash
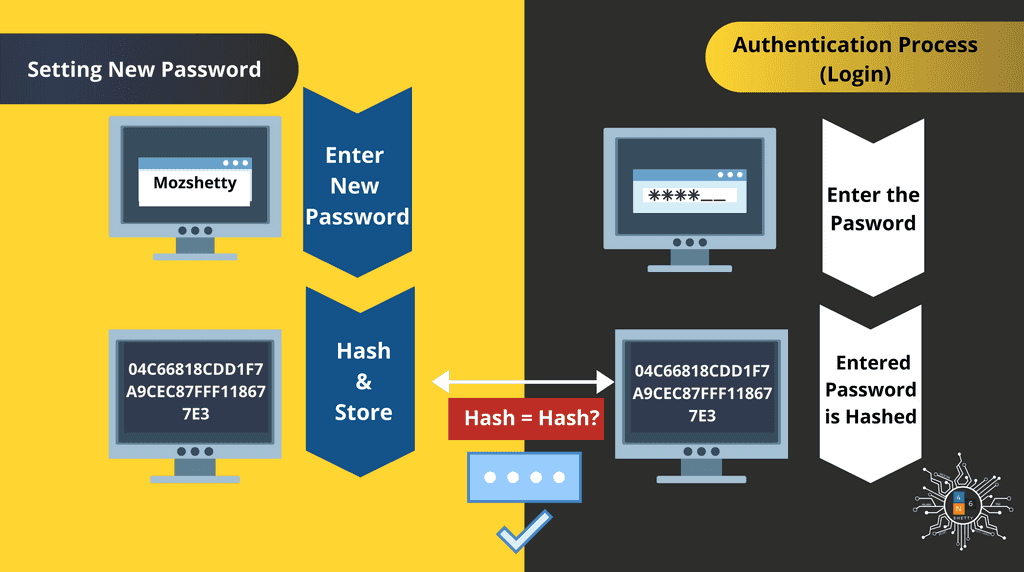
Step1: When you enter new password, it is stored in hash.
Step2: When user logs in to system, the system will produce hash of user password (HashPrime) and comparing the produced hash with stored known user Password hash.
Step 3: If they match the user is authenticated successfully else not.
In next article lets learn more about obtaining and cracking windows password hashes using meterpreter.
Thanks to the training on SANS Sec504 which made me write article on this concept!
Cheers,
MozShetty
